Shoulder pain is a common complaint and physical therapy may be recommended.
Shoulder pain is a common complaint and physical therapy may be recommended as a treatment or as rehabilitation after surgery. Learn about the types of therapy done for different conditions that produce shoulder pain.
The shoulder is a complex ball and socket joint that is made up of the humerus (arm bone), the scapula (shoulder blade) and the clavicle (collarbone). There are numerous ligaments that help 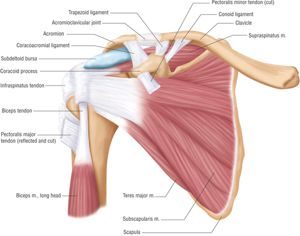 support the shoulder, and many muscular attachments help move the shoulder. The shoulder is an extremely mobile joint, allowing people to reach and move in many directions.
support the shoulder, and many muscular attachments help move the shoulder. The shoulder is an extremely mobile joint, allowing people to reach and move in many directions.
Causes
There are many different causes of shoulder pain. Overhead activities, such as going swimming or tossing a baseball, could cause pinching of the rotator cuff or biceps tendons. Sometimes, poor sitting position may place increased pressure on the make and distress. Injury such as falls or car mishaps can also injure the make. Often, make pain occurs without obvious reason or specific damage. Common make problems include:
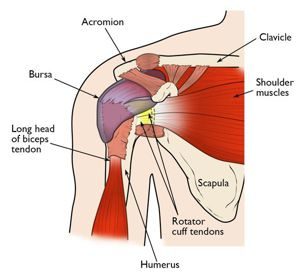
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis: The rotator cuff is several four muscles that help support and move the make. Their principal role is to help contain the ball of the arm bone in the socket as the arm is transferred. The rotator cuff tendons put on the arm bone within an area that is situated straight underneath a bony prominence of the make blade. The tendons can get pinched underneath this bone and be swollen and sore.
Biceps Tendonitis: The biceps tendon attaches your biceps muscle in your upper arm to leading of the make. Many people consider the long mind of the biceps tendon to do something as a fifth rotator cuff tendon, offering balance to leading of the make. This tendon can get pinched by the bony anatomy of the make blade or by ligaments that put on the collarbone and make blade, leading to tendonitis.
Make Bursitis: A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that helps body buildings glide smoothly over each other. There's a bursa that is situated between your humerus bone and the make blade. This bursa can be pinched in the make, resulting in pain.
Frozen Make: Frozen make, or adhesive capsulitis, is a disorder where the shoulder becomes painful and gradually loses motion. This loss of motion can last for up to 18 months; it can be painful and lead to a significant functional loss.
Shoulder Fracture: A shoulder fracture occurs after significant stress. Falling on an outstretched arm is a common cause of a shoulder fracture. The collarbone, scapula, humerus, or a combination of all three may be hurt as a result.
Initial Treatment
 If you have developed shoulder pain consequently of trauma just like a fall or a car accident, you should seek medical attention immediately. Also, if your shoulder pain has lasted for more than two to three weeks and is accompanied by significant practical loss, a visit to your doctor, physical therapist, or another healthcare provider is recommended.
If you have developed shoulder pain consequently of trauma just like a fall or a car accident, you should seek medical attention immediately. Also, if your shoulder pain has lasted for more than two to three weeks and is accompanied by significant practical loss, a visit to your doctor, physical therapist, or another healthcare provider is recommended.
Initially, a brief period of rest is preferred for make pain. This will last 2-3 days. During this time period, you can apply glaciers to the make to help control irritation and offer symptomatic relief. Glaciers can be employed for 15 to 20 minutes. You can even start soft pendulum exercises during this time period. By keeping the make mobile, you can avoid a iced shoulder.
After a couple of days of relax, shoulder exercises can be began to help enhance the flexibility of the joint and enhance the strength of the rotator cuff muscles. As mentioned previously, the rotator cuff helps stabilize the ball in the socket when you lift your arm, so power here's important.
Physical Therapy
A trip to your physical therapist to help evaluate and treat your shoulder pain may be necessary. Your program will likely start with an initial evaluation. During this assessment, the therapist will ask you questions about the nature of your pain and the aggravating and relieving factors. He or she could use a goniometer to consider measurements of the number of movement and power of the make, and monitor the grade of your make movement. Then, special lab tests for the make may be performed to help determine which framework is leading to your pain to help guide treatment.
Following the initial evaluation, treatment will start. Your therapist will choose healing modalities to help control pain or irritation. You might be instructed to execute a home workout program to help enhance the strength and mobility of your shoulder. It is important to follow your physical therapist's advice and instructions closely. Ask questions if you have any.
Additional Treatment
Typically, shoulder pain lasts about four to eight weeks. After a few weeks of treatment, you should notice an improvement in your condition. If you continue to have shoulder pain, you may need to see a specialist. He or she may offer more invasive treatments such as injections or surgery to help treat your shoulder pain.[amazon_link asins='B006GUC9KC,B006VWSWSI,B010MFI9OQ,B003XKRO5S,B071VTQ918,B06X9ZYYKF' template='ProductCarousel' store='idel2moqp01-20′ marketplace='US' link_id='da6c18da-e5ec-11e8-83a4-e3ad22b1484b']
If you need an injection in the shoulder, physical therapy after the injection can help determine the cause of the pain and help avoid future problems. If you do require surgery, follow your surgeon's directions closely to protect the shoulder. Post-operative physical therapy can help regain normal motion and strength after your surgery.
Final Thoughts
You use your shoulders in many types of motion, but they are prone to injury. Appropriate rehab after an injury will help keep the shoulder joint mobile and strong.